Dapr - Creating a User Login/Register Microservice

In an earlier post, I went in more detail how you can utilize Dapr to create a Microservice that communicates over gRPC for quick Inter-Process Communication (IPC).
Now I would like to take this a step further and create a real microservice that allows us to perform account management.
Pre-Requisites
- Dapr installed locally (check with
dapr --version) - Note: you can update with powershell -Command "iwr -useb https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dapr/cli/master/install/install.ps1 | iex"
- Node.js
- CosmosDB
- A Typescript Project as explained in my earlier post here
Note: You can update your Dapr version through one of the following
- Linux:
wget -q https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dapr/cli/master/install/install.sh -O - | /bin/bash - PowerShell:
powershell -Command "iwr -useb https://raw.githubusercontent.com/dapr/cli/master/install/install.ps1 | iex"
Project Scope / Requirements
Scope: Allow us to create users and let them login, returning a JWT token.
Routes:
/user/loginshould return a JWT token/user/registershould create an account
Writing a Hello World route in Express and Typescript
Since Dapr takes care of state management, we are going to write a Microservice that automatically hooks up to this state management (in this case creating and finding our users). But first we have to install our dependencies, so let's install those:
# Dependencies Installation
npm i -S express body-parser isomorphic-fetch express-validator bcrypt uuid
npm i @types/express @types/uuid @types/bcrypt @types/isomorphic-fetch @types/express-validator --save-dev
Whereafter we can add the following code which spins up the server and initializes the route / that will respond with Hello World.
import express = require('express');
const PORT = process.env.APP_HTTP_PORT || 9000;
const PORT_DAPR = process.env.DAPR_HTTP_PORT || 9500;
const app: express.Application = express();
app.get('/', (req, res) => res.send('Hello World'));
app.listen(PORT, () => console.log(`Server started at 0.0.0.0:${PORT}, Dapr at ${PORT_DAPR}`));
Starting this with Dapr on the app port 9000 can be done with:
dapr run --app-id node-api-user --app-port 9000 --port 9500 npm run start
Note: Port 9500 will be used for calling Dapr (e.g. state management)Dapr State Management
Setting up connection to CosmosDB
For our State Management backend we will utilize CosmosDB. To set this up we can refer to the documentation which explains that we should adapt our local created components/statestore.yaml file. When doing this, we end up with this:
apiVersion: dapr.io/v1alpha1
kind: Component
metadata:
name: state-cosmosdb
spec:
type: state.azure.cosmosdb
metadata:
- name: url
value: <YOUR_URL>
- name: masterKey
value: <YOUR_PRIMARY_KEY>
- name: database
value: <YOUR_DB_NAME>
- name: collection
value: <YOUR_COLLECTION_NAME>
Note: For use in production you can create a.yamlfile (e.g.cosmos.yaml) and deploy it withkubectl apply -f cosmos.yaml
After doing this, we are now able to access our state through the DAPR port which we selected during start-up. We can access this through the environment variable DAPR_HTTP_PORT.
Example State Call
We can now store and receive states through http requests. To do this I create a sample.http file which includes the lines I want to send. When then installing the VSCode Extension: REST Client, I am able to utilize CTRL + ALT + R or CTRL + SHIFT + P; > Rest Client: Send Request to send a request.
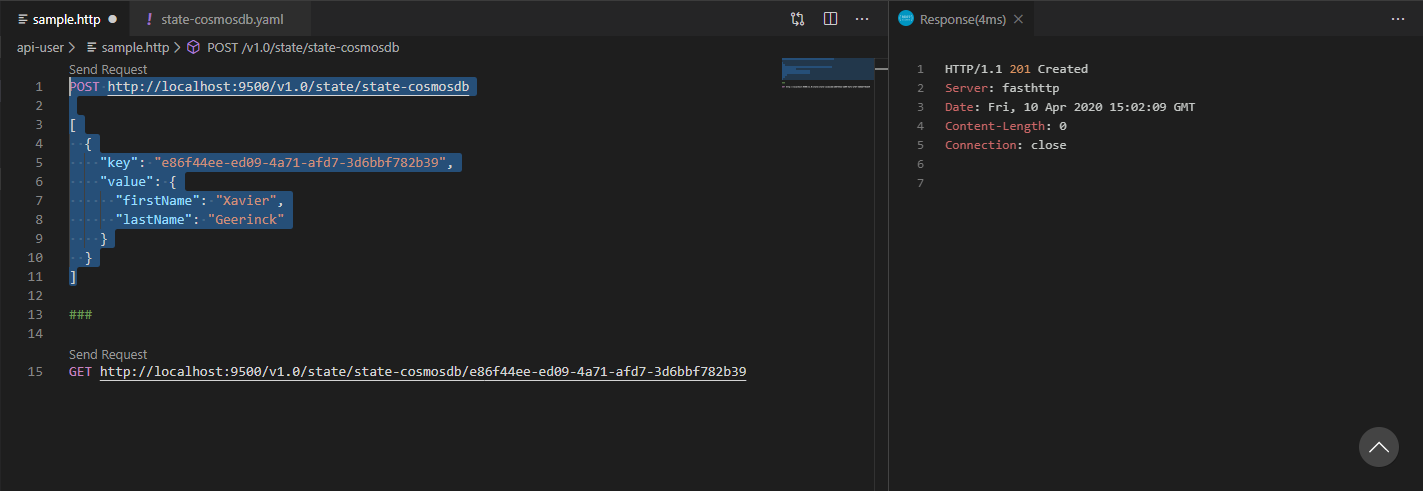
My sample.http file looks like this:
POST http://localhost:9500/v1.0/state/state-cosmosdb
[
{
"id": "e86f44ee-ed09-4a71-afd7-3d6bbf782b39",
"name": "Xavier Geerinck"
}
]
###
GET http://localhost:9500/v1.0/state/state-cosmosdb/e86f44ee-ed09-4a71-afd7-3d6bbf782b39
Whereafter when Running the 2 queries we get the following results (CTRL + ALT + R):
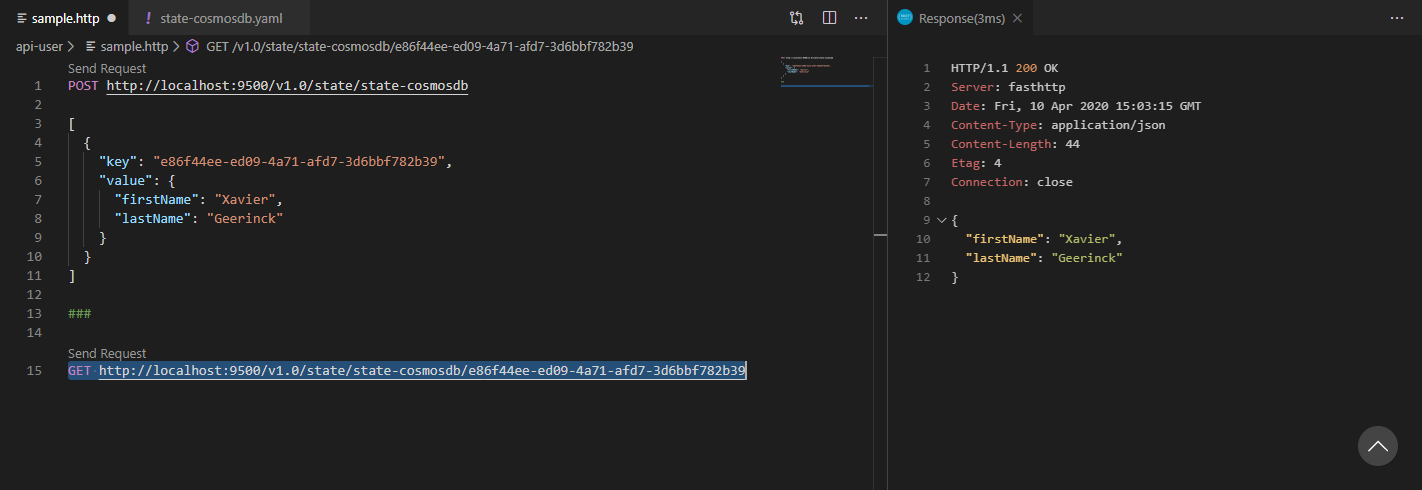
Writing our API Routes with Express
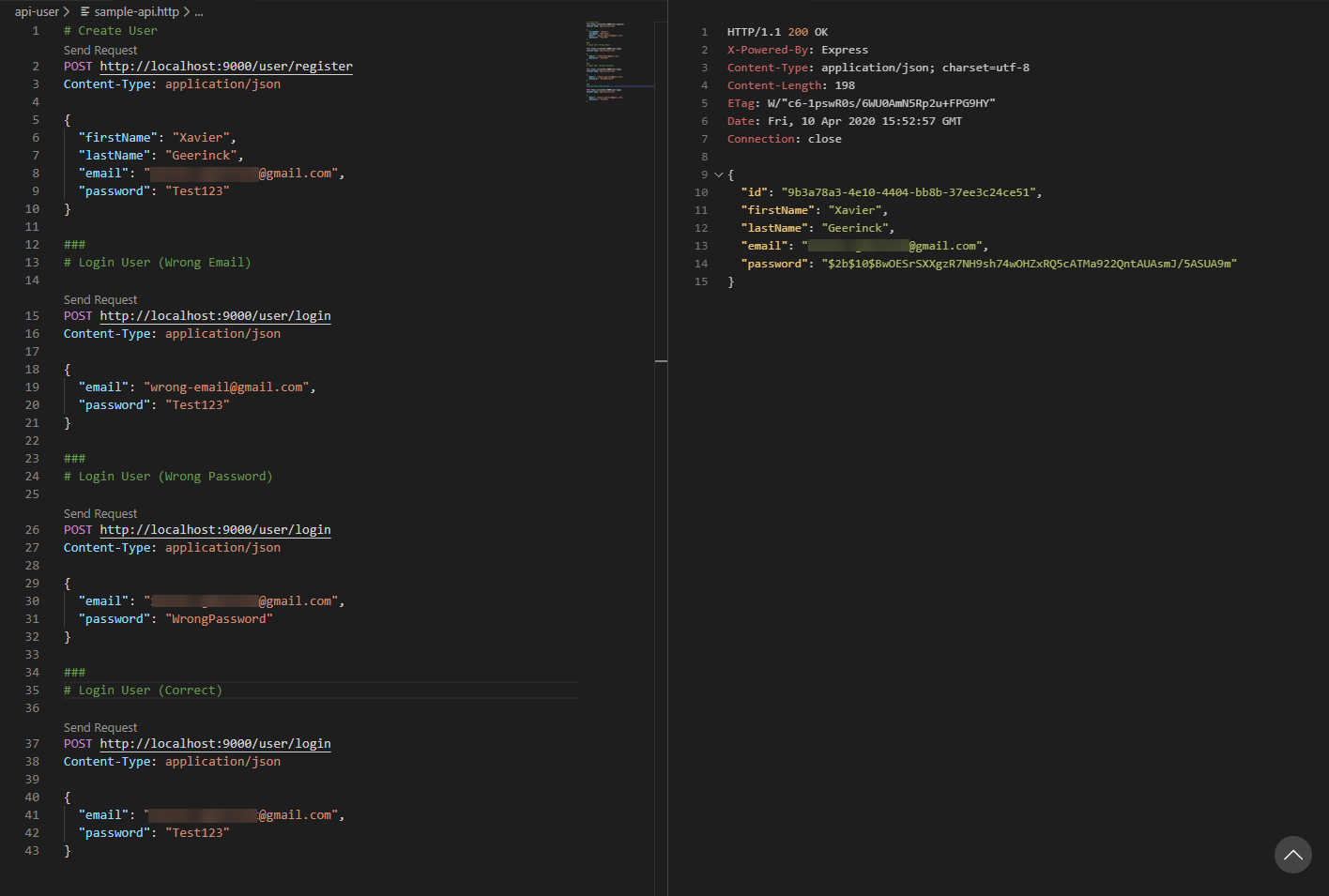
We can now write our API routes with the concepts learned above. When we implement this, we get the following end-result:
import express = require('express');
import { v4 as uuidv4 } from 'uuid';
const bodyParser = require('body-parser');
const { check, validationResult } = require('express-validator');
const bcrypt = require('bcrypt');
const fetch = require('isomorphic-fetch');
const PORT = process.env.APP_HTTP_PORT || 9000;
const PORT_DAPR = process.env.DAPR_HTTP_PORT || 9500;
const DAPR_URL = `http://localhost:${PORT_DAPR}/v1.0`;
const DAPR_URL_STATE = `${DAPR_URL}/state/state-cosmosdb`;
const app: express.Application = express();
app.use(bodyParser.json());
app.listen(PORT, () => console.log(`Server started at 0.0.0.0:${PORT}, Dapr at ${PORT_DAPR}`));
app.post('/user/register', [
check('firstName').isAlpha(),
check('lastName').isAlpha(),
check('email').isEmail(),
check('password').isLength({ min: 6 })
], async (req: express.Request, res: express.Response) => {
const errors = validationResult(req);
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
return res.status(422).json({ errors: errors.array() });
}
try {
// First encrypt password
const bcryptSalt = await bcrypt.genSalt(10);
req.body.password = await bcrypt.hash(req.body.password, bcryptSalt);
// Save User
const userId = uuidv4();
console.log(`Creating user with Id: ${userId}`);
const fetchRes = await fetch(`${DAPR_URL_STATE}`, {
method: 'POST',
body: JSON.stringify([{
key: req.body.email,
value: {
id: userId,
...req.body
}
}]),
headers: {
"Content-Type": "application/json"
}
});
// Handle Response
if (!fetchRes.ok) {
throw "Failed to register user";
}
return res.status(200).send({ success: true, user: {
id: userId,
...req.body
}});
} catch (e) {
return res.status(500).send({ message: e });
}
});
app.post('/user/login', [
check('email').isEmail(),
check('password').isLength({ min: 6 })
], async (req: express.Request, res: express.Response) => {
const errors = validationResult(req);
if (!errors.isEmpty()) {
return res.status(422).json({ errors: errors.array() });
}
try {
// Find existing user
const fetchRes = await fetch(`${DAPR_URL_STATE}/${req.body.email}`);
// Handle Response
if (!fetchRes.ok) {
throw "Failed to find user";
}
const fetchResUser = await fetchRes.json();
// Check password
const bcryptResult = await bcrypt.compare(req.body.password, fetchResUser.password);
if (!bcryptResult) {
throw "Incorrect password";
}
return res.status(200).send(fetchResUser);
} catch (e) {
return res.status(500).send({ message: e });
}
});

Member discussion